1. Introdução
Pigmented lesions such as birthmarks and dark spots affect millions worldwide, impacting appearance and psychological well-being. Traditional treatments—cryotherapy, dermabrasion, and surgical excision—often led to scarring and uneven pigment results. The advent of laser therapy, particularly through selective photothermolysis, marked a major breakthrough but early nanosecond systems still carried risks of dyspigmentation and extended recovery. Pico laser technology, with ultra-short pulses measured in trillionths of a second, delivers precise photomechanical energy that shatters pigment clusters with minimal thermal damage. This allows faster clearance, shorter treatment times, and improved safety for darker skin tones and resistant pigmentation. As a result, Pico laser has become a leading solution for managing congenital and acquired pigmentary conditions, including birthmarks, melasma, lentigines, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. This article explores how Pico laser achieves visible results, influencing factors, and emerging innovations in modern pigmentation management.
2. Understanding Pico Laser Technology
Before examining the clinical applications and benefits of pico laser treatment, it is essential to understand the fundamental technology that distinguishes these advanced systems from their predecessors and enables their superior performance in pigmentation management. This foundation provides context for appreciating how picosecond lasers achieve visible results where previous technologies often fell short.
2.1 What Is Pico Laser?
Pico laser technology delivers ultra-short energy pulses measured in picoseconds—one trillionth of a second—offering a major advancement over traditional nanosecond Q-switched lasers. Operating across multiple wavelengths (532, 730, 755, 785, and 1064 nm), it allows precise targeting of different pigmentation depths and melanin absorption profiles. Modern systems often feature diffractive or fractional lens arrays that create focused microspots for both localized lesion treatment and broad skin rejuvenation. This photomechanical approach minimizes thermal damage while maximizing pigment fragmentation efficiency. Adjustable parameters such as fluence, spot size, pulse rate, and treatment passes provide clinicians with exceptional flexibility to tailor treatments for various skin types and pigmentation concerns. As a result, pico lasers achieve safer, faster, and more predictable outcomes for conditions ranging from freckles and melasma to congenital birthmarks, representing a new standard in aesthetic dermatology and pigment correction.
2.2 How Pico Laser Works on Pigmented Skin
The pico laser’s effectiveness lies in its photomechanical rather than photothermal action on melanin. Ultra-short picosecond pulses deliver rapid bursts of energy that generate high-pressure photoacoustic waves, shattering melanosomes into ultra-fine pigment fragments much smaller than those produced by older nanosecond lasers. This minimizes heat diffusion and protects surrounding skin from burns or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Scientific studies have defined wavelength-specific fluence thresholds for optimal pigment disruption, ensuring precise and safe treatment parameters. The fragmented pigment particles are efficiently cleared by dermal macrophages and lymphatic drainage, accelerating visible pigment reduction. Meanwhile, laser-induced optical breakdown and dermal cavitation trigger controlled healing responses that stimulate collagen production and skin remodeling without damaging the epidermis. Together, these mechanisms explain the pico laser’s superior ability to fade pigmentation while simultaneously rejuvenating skin texture and tone with minimal risk or downtime.
2.3 Types of Skin Conditions Treatable by Pico Laser
Nevus of Ota / Ito: Achieves up to 75% pigment clearance with precise melanin targeting.
Café-au-lait Macules: Respond well to pico laser with low recurrence risk.
Melasma: Improves significantly with multi-wavelength or combination treatments.
Solar Lentigines (Age Spots): Lightens effectively and enhances skin clarity.
Freckles (Ephelides): Fade quickly with minimal irritation or downtime.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Safely reduces discoloration from acne or inflammation.
Hori’s Nevus: Deep dermal pigment responds well to 1064 nm wavelengths.
Tattoo Pigment: Breaks down multi-color ink efficiently in fewer sessions.
Enlarged Pores: Stimulates collagen to refine and smooth skin texture.
Fine Lines and Scars: Promotes neocollagenesis for firmer, rejuvenated skin.
3. Clinical Benefits of Pico Laser for Birthmarks and Dark Spots
Understanding the specific advantages that pico laser technology provides compared to alternative treatments helps clarify why it has become the preferred modality for many dermatologists and patients seeking pigmentation correction. The clinical benefits extend beyond simple pigment removal to encompass safety, efficiency, and comprehensive skin quality improvement.
3.1 Visible Pigment Reduction
Clinical evidence consistently confirms that pico laser therapy produces significant pigment reduction across various birthmarks and dark spots. Objective analyses such as VISIA imaging reveal measurable decreases in melanin density, fewer pigmented lesions, and enhanced overall complexion uniformity. Comparative trials show that picosecond systems—particularly the 755 nm alexandrite pico laser—achieve faster clearance, higher patient satisfaction, and shorter recovery than nanosecond Q-switched lasers. Even a single treatment can yield visible improvements, though optimal outcomes usually require multiple sessions spaced several weeks apart. The ultra-short pulse duration fragments melanin into smaller particles that the body clears naturally, leading to smoother, brighter, and more even-toned skin. For patients, the noticeable reduction in discoloration and clearer skin tone translates into both clinical success and greater cosmetic satisfaction.
3.2 Minimal Downtime and Safety
Pico laser therapy offers exceptional safety and minimal downtime compared with older laser systems or ablative treatments. Its photomechanical mechanism minimizes heat diffusion, reducing post-procedure inflammation, redness, and swelling. Most patients recover within hours to a few days and can resume normal activities almost immediately. Adverse effects such as transient PIH, petechiae, or mild textural changes are rare when proper parameters are used. Importantly, pico laser is well-tolerated across all Fitzpatrick skin types, including darker tones where conventional lasers carry higher risks of pigment alteration or scarring. This broadened safety margin makes treatment accessible to a wider range of patients. The combination of efficacy, comfort, and quick recovery positions pico laser as a leading choice for pigment correction without disrupting daily routines.
3.3 Stimulates Collagen and Skin Rejuvenation
Beyond pigment clearance, pico laser technology triggers dermal regeneration through precise photomechanical stimulation. The ultra-short pulses create micro-injuries that activate fibroblast activity, promoting collagen and elastin synthesis while preserving the epidermis. Fractional pico systems with diffractive lens arrays have shown measurable improvements in fine lines, pore size, and overall skin texture. These rejuvenation effects enhance firmness, elasticity, and luminosity, complementing pigment correction to deliver comprehensive aesthetic improvement. Patients not only experience clearer, more even skin tone but also smoother, younger-looking complexion. This dual action—pigment reduction and collagen remodeling—distinguishes pico laser from traditional pigment-focused devices, offering a holistic approach that addresses both discoloration and early aging concerns within a single, minimally invasive treatment framework.
3.4 Psychological and Social Benefits
The benefits of pico laser treatment extend beyond skin tone correction to significant emotional and social well-being. Pigmented lesions often cause self-consciousness, reduced confidence, and social withdrawal. Successful pigment reduction visibly improves appearance, which can alleviate anxiety, boost self-esteem, and restore social comfort. Studies show that patients report enhanced mood, better interpersonal relationships, and greater satisfaction with their professional image after treatment. For individuals who previously relied on heavy makeup to conceal pigmentation, the ability to appear naturally clear-skinned brings psychological relief and convenience. In children or adolescents with visible birthmarks, early treatment may prevent long-term self-image issues and social stigmatization. Overall, pico laser’s visible results contribute not only to aesthetic improvement but also to restored confidence and improved quality of life.
4. Factors Influencing Pico Laser Treatment Results
While pico laser technology offers powerful capabilities for pigmentation management, treatment outcomes vary considerably among individuals based on multiple patient-specific and lesion-specific variables. Understanding these influencing factors enables realistic expectation setting, appropriate patient selection, and protocol optimization to maximize success rates and minimize complications.
4.1 Skin Type and Pigmentation Depth
Skin phototype strongly determines pico laser strategy and safety. Lighter Fitzpatrick skin (I–III) commonly tolerates higher fluences and typically shows predictable pigment clearance with a relatively low risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). Darker phototypes (IV–VI) require conservative starting settings, test patches, and gradual energy escalation because melanocyte overstimulation can provoke paradoxical darkening. Pigment depth is equally important: epidermal pigmentation clears faster because melanosomes are superficial, whereas dermal melanocytosis needs longer wavelengths (for example 1064 nm) to reach deeper deposits. Mixed-depth conditions such as melasma often demand staged or combination approaches addressing both layers. Clinicians should individualize pulse duration, spot size, and energy based on skin type and depth assessment, document baseline photography and objective imaging, and plan follow-up to adjust parameters safely for optimal, reproducible results.
4.2 Size, Location, and Type of Lesion
Lesion characteristics fundamentally affect treatment complexity and outcomes. Small, well-circumscribed lesions typically require fewer sessions because the pigment burden is lower and macrophage-mediated clearance is more efficient. Large or confluent patches necessitate staged treatment and careful mapping to ensure consistent energy delivery across the area. Anatomical location matters: facial areas often respond well due to thinner epidermis and richer vascular supply, yet their cosmetic importance requires more conservative parameters to minimize visible side effects. Conversely, thicker skin on the trunk may tolerate higher energies but heal differently. Lesion morphology—including border regularity seen in café-au-lait variants—predicts prognosis: irregular “coast of Maine” lesions often clear better than smooth “coast of California” types. Understanding size, depth, location, and morphology allows clinicians to set realistic expectations and optimize session planning and parameter selection.
4.3 Age and Skin Health
Age and baseline skin health influence both the speed of recovery and the durability of pico laser results. Younger skin tends to have faster epidermal turnover, more active fibroblasts, and stronger collagen remodeling capacity, which can accelerate pigment clearance and enhance complementary rejuvenation effects. Early intervention for certain congenital birthmarks may therefore produce superior cosmetic outcomes, although pediatric treatments require specialized dosing, analgesia planning, and psychosocial considerations. Older patients may present with cumulative photodamage, decreased repair capacity, and slower epidermal renewal, which can extend the time to visible improvement; however, age alone is not a contraindication. Pre-treatment optimization—improving hydration, repairing barrier function, treating active inflammation, and addressing comorbid skin conditions—improves tolerance and reduces complication risk, so clinicians should assess and enhance skin health before initiating laser protocols.
4.4 Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Environmental exposure and daily habits strongly modulate pico laser efficacy and the longevity of results. Ultraviolet radiation is the most critical modifiable variable: even brief unprotected sun exposure post-treatment can reactivate melanogenesis and undermine clearance, so rigorous photoprotection (broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen, hats, and avoidance of peak UV hours) is essential. Hormonal influences—pregnancy, contraceptive use, and endocrine disorders—can exacerbate melasma and increase recurrence risk, making timing of elective treatments important. Smoking impairs microcirculation and delays healing, while poor sleep and inadequate nutrition can worsen inflammatory profiles and slow pigment clearance. Counseling patients on sun avoidance, smoking cessation, stress management, sleep quality, and antioxidant-rich nutrition enhances treatment responsiveness and helps sustain long-term aesthetic gains following pico laser therapy.
4.5 Compliance and Aftercare Practices
Adherence to preconditioning regimens and meticulous aftercare is pivotal to maximizing safety and efficacy. Pre-treatment skin conditioning—topical agents such as hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C—can downregulate melanocyte activity and improve laser responsiveness when medically supervised. After treatment, patients should follow gentle cleansing, barrier repair with emollients, and targeted anti-inflammatory care while strictly avoiding sun exposure and irritant products. Noncompliance—skipping sunblock, premature exfoliation, or returning to harsh topical regimens too early—raises the risk of PIH and undermines clearance. Scheduled follow-ups allow clinicians to monitor progress, perform test patches if responses are atypical, and adapt energy settings or interval timing. Clear written instructions, photographic documentation, and regular reminders increase adherence and convert good procedural outcomes into durable, satisfactory results.
4.6 Individual Healing Response
Biological variability in immune function, wound healing, and pigment metabolism creates substantial inter-patient differences in response to pico laser treatment. Genetic polymorphisms in melanogenesis enzymes, differential expression of inflammatory cytokines, and variable collagen remodeling rates influence both how quickly fragmented pigment is cleared and how susceptible a patient is to adverse events. Efficient macrophage phagocytosis and intact lymphatic drainage accelerate removal of ultrafine pigment particles, while systemic factors—immunosuppression, chronic illness, certain medications—can slow progress and increase complications. Psychological stress, sleep deprivation, and nutritional deficits also modulate inflammatory and repair pathways. Because of this heterogeneity, clinicians should adopt flexible, patient-specific protocols, use in-office test spots, monitor objective metrics and photos, and adjust treatment pacing and supportive care to match each patient’s individualized healing trajectory.
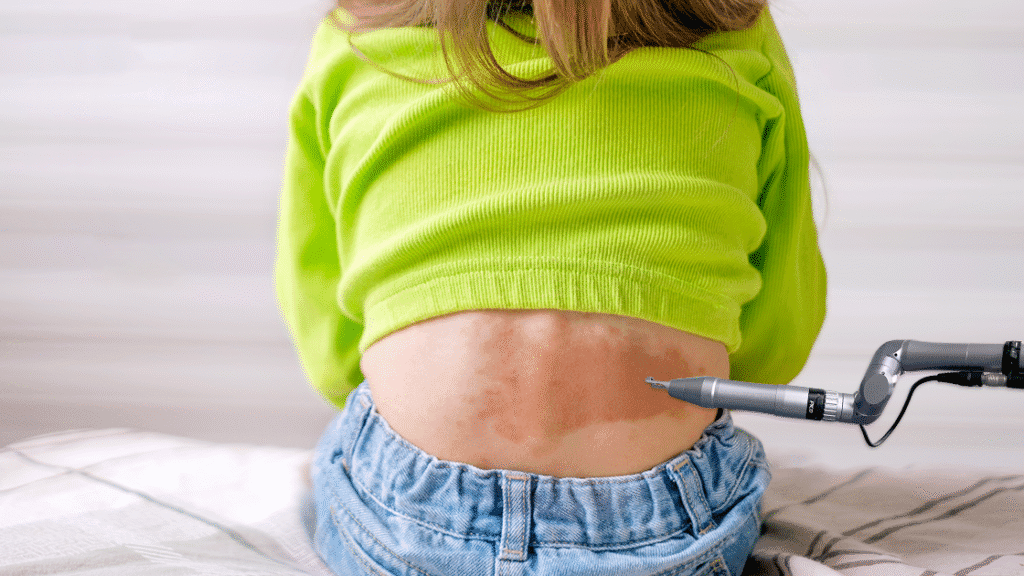
5. Advanced Applications and Emerging Trends
As pico laser technology continues evolving and clinical experience expands, practitioners are developing innovative protocols and identifying new applications that push beyond traditional pigmentation treatment paradigms. These advanced approaches and emerging trends represent the cutting edge of laser dermatology, offering solutions for previously intractable cases and enhanced outcomes through strategic combinations.
5.1 Combination Therapies for Enhanced Results
Combining pico laser with other modalities provides synergistic benefits for complex pigmentation disorders. Sequential protocols that pair picosecond laser sessions with topical depigmenting agents such as hydroquinone, kojic acid, or tranexamic acid suppress melanogenesis after pigment fragmentation, achieving faster clearance and lower recurrence than monotherapy. Oral tranexamic acid enhances results in melasma by modulating vascular and inflammatory factors. Chemical peels performed between laser sessions can target superficial pigmentation layers, while pico laser penetrates deeper melanin deposits. Fractional radiofrequency or microneedling further stimulate collagen remodeling and improve absorption of brightening actives. These multi-layered strategies require precise timing and medical oversight to prevent over-inflammation or pigment rebound but deliver visibly superior, longer-lasting results for resistant pigmentation when integrated into structured treatment plans supervised by experienced dermatologists or aesthetic physicians.
5.2 Treatment of Challenging or Resistant Pigmented Lesions
Pico laser technology has transformed management of pigmentary disorders previously resistant to conventional therapy. Low-fluence, high-frequency picosecond “laser toning” using 1064 nm wavelength offers gradual pigment reduction for melasma while minimizing thermal inflammation and rebound. Newer 730 nm titanium sapphire systems improve melanin selectivity and show progress in difficult café-au-lait macules. Patients with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially darker phototypes, can now be treated safely through cautious energy titration and rigorous aftercare. Dermal melanocytosis or lesions unresponsive to nanosecond lasers often benefit from optimized picosecond fluences and extended protocols. These refinements—based on clinical evidence and histologic insight—extend the range of treatable pigment disorders while maintaining safety. Continuous adaptation of wavelength, fluence, and repetition rate allows dermatologists to personalize protocols, achieving pigment lightening that was once unattainable without scarring or recurrence.
5.3 Technological Innovations in Pico Laser
Recent advances are reshaping pico laser technology and expanding its versatility. Multi-wavelength platforms now integrate 532, 730, 755, and 1064 nm options in one system, enabling tailored depth-specific targeting for different pigment types. Fractional delivery optics with adjustable density and pattern improve precision, reduce downtime, and enhance dermal remodeling. Built-in cooling systems maintain patient comfort and safety during higher-fluence sessions. Artificial-intelligence-assisted algorithms are emerging to analyze patient images and automatically suggest optimal parameters, reducing operator variability. Research into even shorter femtosecond-range pulses promises more efficient pigment fragmentation with minimal heat diffusion. Future tunable laser technologies could continuously adjust wavelength to match individual chromophore absorption peaks, providing unmatched customization. Together, these innovations are elevating treatment predictability, safety, and clinical efficiency—marking a new era of precision pigmentation therapy in dermatology.
6. Evidence, Research, and Expert Opinions
The clinical adoption of any medical technology should be grounded in rigorous scientific evidence, expert consensus, and real-world validation. Examining the research foundation supporting pico laser efficacy, safety, and optimal utilization provides essential context for evidence-based decision-making by practitioners and patients considering this treatment modality.
6.1 Clinical Studies Supporting Pico Laser
Growing clinical evidence validates the efficacy of pico laser for treating diverse pigmentation disorders. A 2024 randomized controlled trial using 755-nm alexandrite picosecond laser for facial lesions showed significant melanin reduction and improved VISIA parameters regardless of patient demographics. Split-face studies consistently demonstrate that picosecond lasers outperform nanosecond Q-switched systems in pigment clearance, safety, and patient satisfaction. Research on melasma yields mixed results, reflecting its multifactorial nature, but fractional pico approaches remain promising when combined with maintenance protocols. Long-term follow-ups confirm sustained improvements up to three years post-treatment with minimal recurrence. Emerging meta-analyses further consolidate these findings, identifying wavelength choice, energy fluence, and treatment interval as key determinants of success. Collectively, these studies provide strong evidence supporting pico laser as an advanced, evidence-based solution for pigmentation management and skin rejuvenation across varied phototypes.
6.2 Insights from Dermatologists and Laser Specialists
Experienced dermatologists emphasize comprehensive assessment and individualized planning as cornerstones of successful pico laser treatment. Proper lesion evaluation, skin typing, and history taking—including hormonal, genetic, and environmental factors—ensure accurate protocol selection and reduced complication risks. Experts caution that while pico laser offers clear advantages over older systems, it is not universally curative; realistic expectations regarding treatment sessions, clearance potential, and recurrence prevention must be set. Optimal outcomes depend on correct fluence, uniform overlap, and recognition of treatment endpoints to prevent overtreatment. Practitioners also highlight that pico laser performs best when integrated into holistic pigmentation management—combining sun protection, topical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Consensus across experts reinforces flexibility and ongoing parameter refinement based on individual response, establishing pico laser as an effective but context-dependent tool requiring clinical expertise for safe, lasting results.
6.3 Real-World Testimonials
Patient testimonials offer valuable context to clinical data, revealing high satisfaction with pico laser’s visible pigment reduction and rapid recovery. Individuals treated for freckles, solar lentigines, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation frequently report smoother, clearer skin and renewed confidence. Patients with congenital birthmarks like nevus of Ota often describe life-changing emotional relief after treatment success. Most highlight manageable discomfort and minimal downtime, allowing normal routines immediately post-procedure. However, patients with chronic or complex conditions such as melasma sometimes express disappointment when outcomes are partial or relapse occurs—underscoring the importance of realistic pre-treatment counseling and strict aftercare adherence. Positive feedback typically credits practitioner expertise, detailed explanation, and supportive follow-up, whereas negative experiences often stem from miscommunication, inadequate preparation, or non-compliance with post-treatment guidelines. These accounts reinforce that patient education and personalization are key to achieving satisfying, sustainable results.
7. Conclusão
Tecnologia laser Pico marks a major advancement in treating birthmarks and dark spots, combining precision, safety, and efficacy unmatched by earlier nanosecond systems. Its photomechanical energy delivery shatters melanin into finer particles with minimal heat damage, enabling faster pigment clearance and safer treatment for all skin types. Clinical studies confirm significant improvements across diverse conditions such as nevus of Ota, café-au-lait macules, melasma, and lentigines, with measurable gains in pigment reduction and skin texture. Benefits extend beyond pigmentation correction—patients experience minimal downtime, collagen stimulation, and psychological relief through renewed confidence. Successful outcomes rely on proper patient selection, customized protocols, and strict sun protection. Ongoing innovations and combination therapies continue enhancing efficacy for resistant lesions. Supported by strong research and expert consensus, pico laser stands as the gold standard for modern pigmentation management and holistic skin rejuvenation.
8. Referências
- Evaluation of the Efficacy of the 755 nm Picosecond Laser in Eliminating Pigmented Skin Lesions after a Single Treatment Based on Photographic Analysis with Polarised Light
- Association between irradiation parameters and outcomes for picosecond laser treatment of nevus of Ota: An in-silico-supported meta-analysis
- Advancements in Laser Therapies for Dermal Hyperpigmentation in Skin of Color: A Comprehensive Literature Review and Experience of Sequential Laser Treatments in a Cohort of 122 Indian Patients
- Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of the dual wavelength picosecond laser for the treatment of benign pigmented lesions in Asians








