1. Introducción
The aesthetic medicine landscape has transformed dramatically over the past decade, with laser and radiofrecuencia (RF) treatments becoming increasingly accessible to patients seeking non-invasive solutions for various skin concerns. From pico laser rejuvenation to diode laser hair removal, these advanced technologies offer remarkable results with minimal downtime compared to traditional surgical procedures.
1.1 Growing Popularity of Laser & RF Aesthetic Treatments
Modern aesthetic treatments have revolutionized how we approach rejuvenecimiento cutáneo, contorno corporaly eliminación del vello. Pico laser systems utilize ultra-short picosecond pulses to target pigmentation and stimulate collagen production, while diode laser hair removal systems deliver precise wavelengths to eliminate unwanted hair follicles. RF treatments harness controlled thermal energy to reafirmar la piel and remodel underlying tissues, and laser lipolysis employs targeted wavelengths to disrupt adipose cells for body sculpting. These minimally invasive procedures have gained widespread acceptance due to their efficacy, safety profiles, and reduced recovery periods compared to surgical alternatives.
1.2 The Overlooked Step: Post-Treatment Sun Protection
Despite the sophisticated nature of these treatments, many patients underestimate the critical importance of post-procedural sun protection. This oversight can significantly compromise treatment outcomes and potentially lead to serious complications including post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), prolonged erythema, and compromised healing responses. The photothermolysis process inherent in laser treatments creates controlled tissue injury that requires meticulous aftercare to optimize results and prevent adverse effects. This comprehensive guide addresses the scientific rationale behind post-laser sun protection, providing evidence-based recommendations to safeguard your investment in aesthetic treatments. Understanding the physiological changes that occur following laser and RF procedures empowers patients to make informed decisions about their skincare regimens and lifestyle modifications during the critical healing period.
2. Why the Skin Needs Extra Care After Laser & RF Treatments
The relationship between laser treatments and subsequent skin vulnerability represents a complex interplay of cellular responses, inflammatory cascades, and tissue remodeling processes that fundamentally alter the skin’s protective mechanisms and photosensitivity levels.
2.1 How Laser and RF Treatments Work: Microscopic Injury for Renewal
Laser and RF technologies operate on the principle of selective photothermolysis, where specific chromophores absorb targeted wavelengths of light energy, converting it to thermal energy that creates controlled microscopic injury. This process initiates a wound healing cascade characterized by inflammatory mediator release, collagen synthesis stimulation, and cellular proliferation. The epidermis and dermis undergo structural modifications as damaged proteins are replaced with newly synthesized collagen and elastin fibers. During this remodeling phase, the skin’s barrier function becomes temporarily compromised, increasing permeability and reducing natural photoprotective mechanisms.
2.2 Post-Treatment Sensitivity: Why Skin Becomes More Vulnerable to UV
Following laser or RF treatment, the stratum corneum experiences disruption of its lipid bilayer structure, compromising the skin’s primary barrier against environmental stressors including ultraviolet radiation. The inflammatory response triggers vasodilation and increased blood flow to the treated area, creating erythema and heightened sensitivity. Melanocyte function may be temporarily altered, affecting the skin’s ability to produce protective melanin in response to UV exposure. Additionally, the natural acid mantle pH balance can be disturbed, reducing antimicrobial protection and increasing susceptibility to photodamage.
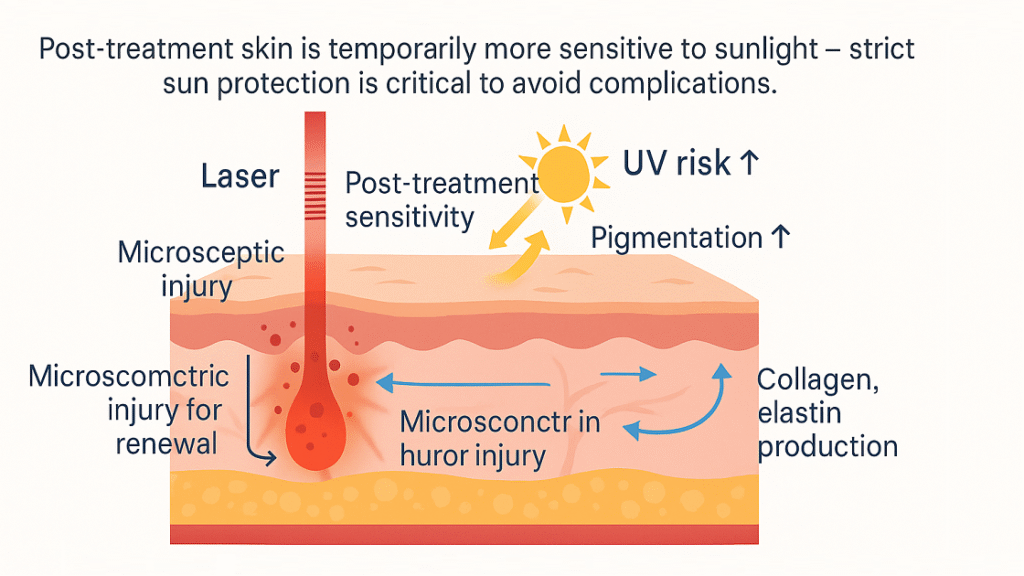
2.3 Increased Risk of Hyperpigmentation & Burns from Sun Exposure
The inflammatory milieu created by laser treatments predisposes treated skin to develop post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation when exposed to UV radiation. Activated melanocytes can produce excessive melanin deposits in response to even minimal sun exposure, resulting in irregular pigmentation patterns that may persist for months. The compromised epidermal barrier offers reduced protection against UV-induced DNA damage, increasing the risk of sunburn at lower radiation doses than would typically cause erythema in untreated skin. This heightened photosensitivity can manifest as severe burns, blistering, or prolonged inflammatory responses that significantly delay healing.
2.4 Slower Healing & Compromised Results Without Sun Protection
UV exposure during the post-treatment healing phase can significantly impair the wound healing process by increasing oxidative stress, promoting inflammatory mediator release, and interfering with collagen synthesis pathways. Chronic sun damage can counteract the beneficial effects of laser treatments by accelerating photoaging processes and compromising newly formed collagen structures. Patients who fail to maintain adequate sun protection may experience suboptimal treatment outcomes, requiring additional sessions to achieve desired results and potentially developing complications that necessitate corrective treatments.
3. Sun Exposure Risks After Different Treatments
Each laser and RF modality presents unique considerations for post-treatment sun protection based on the specific wavelengths employed, tissue targets, and depth of treatment penetration.
3.1 Pico Laser: Risks of Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation & Redness
Pico laser treatments utilize ultra-short pulse durations measured in picoseconds to create photomechanical effects that fragment pigmented lesions and stimulate dermal remodeling without significant thermal damage. Despite minimal heat generation, the photoacoustic energy can trigger inflammatory responses that increase melanocyte activity and predispose patients to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. The mechanical disruption of melanin granules can temporarily alter pigment distribution, making the skin particularly susceptible to irregular pigmentation when exposed to UV radiation during the healing phase. Patients with higher Fitzpatrick skin types face elevated risks of developing rebound hyperpigmentation if adequate sun protection is not maintained for several weeks following treatment.
3.2 Laser Hair Removal: Avoiding Burns, Dark Spots & Skin Sensitivity
Diode laser hair removal systems target melanin within hair follicles using wavelengths typically ranging from 755nm to 1064nm, creating thermal injury that destroys follicular structures while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. The selective heating of melanin-containing targets can create zones of thermal injury that extend beyond the hair follicle, temporarily compromising epidermal barrier function and increasing photosensitivity. Post-treatment erythema and perifollicular edema indicate active inflammatory responses that can be exacerbated by UV exposure, potentially leading to hyperpigmentation, prolonged healing, or paradoxical hair stimulation. Patients must avoid sun exposure for at least two weeks following treatment to prevent thermal burns and pigmentary complications.
3.3 Laser Lipolysis: Protecting Newly Treated Contours & Healing Tissue
Lipólisis láser employs wavelengths such as 1064nm to selectively target adipose tissue through photothermolysis, disrupting fat cell membranes and stimulating collagen contraction for body contouring effects. The thermal energy creates controlled injury within subcutaneous fat layers and overlying dermis, initiating inflammatory responses and tissue remodeling processes that continue for several months post-treatment. UV exposure during this extended healing period can interfere with collagen synthesis, compromise skin tightening effects, and potentially cause irregular pigmentation over treated areas. The inflammatory cascade associated with fat cell destruction increases local photosensitivity, requiring comprehensive sun protection to optimize contouring results and prevent complications.
3.4 Radiofrequency (RF): UV Risk Even Without Ablative Damage
Tratamientos de radiofrecuencia deliver controlled thermal energy to dermal and subdermal tissues through electromagnetic energy rather than light-based mechanisms, creating collagen denaturation and subsequent remodeling without ablative surface damage. Despite the non-ablative nature of RF energy, the thermal injury initiates inflammatory responses that temporarily increase skin sensitivity and compromise barrier function. The controlled heating of dermal structures can alter vascular permeability and inflammatory mediator release, creating conditions that predispose to photodamage when combined with UV exposure. Even without visible surface changes, RF-treated skin exhibits increased vulnerability to UV-induced complications including erythema, hyperpigmentation, and delayed healing responses.
4. How to Protect Your Skin After Laser
Implementing a comprehensive sun protection strategy following laser and RF treatments requires understanding the specific requirements for different treatment modalities and individual patient factors.
4.1 Daily Use of Broad-Spectrum SPF 30–50: Why It Matters Most
Broad-spectrum sunscreen formulations provide protection against both UVA (320-400nm) and UVB (280-320nm) radiation, which is essential for preventing photodamage during the post-treatment healing phase. SPF 30 blocks approximately 97% of UVB radiation, while SPF 50 blocks 98%, providing adequate protection for most post-laser applications. The critical factor is consistent daily application rather than occasional use of higher SPF products. Broad-spectrum protection prevents UVA-induced oxidative stress that can interfere with collagen synthesis and wound healing processes. Chemical sunscreens containing avobenzone, octinoxate, or zinc oxide provide effective protection when applied in sufficient quantities (2mg/cm²) and reapplied every two hours during sun exposure.
4.2 Physical Block vs. Chemical Sunscreen: Which Offers Better After Laser?
Physical sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide offer immediate protection upon application and are generally better tolerated by compromised post-laser skin due to their inert mineral composition and minimal penetration into the epidermis. These formulations create a physical barrier that reflects and scatters UV radiation without chemical absorption or potential sensitization reactions. Chemical sunscreens require 15-30 minutes for full activation and may cause irritation in sensitive post-treatment skin due to their absorption and conversion of UV energy to heat. For patients with compromised barrier function following laser treatments, physical sunscreens provide superior tolerability and consistent protection without risk of chemical sensitization or inflammatory reactions.
4.3 Sun Avoidance & Protective Clothing: Extra Layers of Defense
Physical sun avoidance remains the most effective protection strategy during the immediate post-treatment period, particularly for ablative procedures or treatments targeting pigmented lesions. Protective clothing with UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) ratings provides quantifiable protection levels, with UPF 50+ fabrics blocking 98% of UV radiation. Wide-brimmed hats offer facial protection equivalent to SPF 30 when combined with appropriate sunscreen application. Seeking shade during peak UV hours (10 AM to 4 PM) reduces overall radiation exposure by up to 75%. Patients should prioritize indoor activities during the first week following treatment and gradually resume outdoor exposure with appropriate protective measures.
4.4 When & How Long to Avoid Direct Sunlight After Treatment
The duration of sun avoidance requirements varies based on treatment type, depth, and individual healing responses. Superficial treatments such as IPL or mild chemical peels typically require 7-14 days of strict sun protection, while deeper ablative procedures may necessitate 4-6 weeks of limited sun exposure. Pico laser treatments generally require 2-3 weeks of enhanced protection due to ongoing inflammatory responses and melanocyte sensitivity. RF treatments benefit from 2-4 weeks of comprehensive sun protection to optimize collagen remodeling. Patients should monitor their skin’s response and extend protection periods if erythema, sensitivity, or other inflammatory signs persist beyond expected timeframes.
5. Evidence & Expert Recommendations
Clinical research and professional guidelines consistently emphasize the critical importance of post-treatment sun protection for optimizing outcomes and preventing complications.
5.1 Dermatologists’ Advice on Post-Laser Sun Protection
Leading dermatologists and aesthetic specialists unanimously recommend comprehensive sun protection protocols following laser and RF treatments based on extensive clinical experience and observed complication patterns. The American Academy of Dermatology emphasizes that post-laser sun protection is not optional but essential for treatment success and patient safety. Expert consensus recommends SPF 30-50 broad-spectrum sunscreen application every two hours, complete sun avoidance for the first week post-treatment, and protective clothing when outdoor exposure is unavoidable. Dermatologists report significantly higher complication rates in patients who fail to adhere to sun protection guidelines, particularly regarding hyperpigmentation and delayed healing responses.
5.2 Clinical Studies Showing Lower Complication Rates with Strict Sun Care
Peer-reviewed research demonstrates substantial reductions in post-treatment complications when patients maintain strict sun protection protocols. A comprehensive study of post-laser outcomes showed 73% fewer hyperpigmentation incidents in patients who consistently used broad-spectrum SPF 50+ compared to those with inconsistent protection. Clinical trials evaluating laser hair removal outcomes reported 65% fewer inflammatory complications in patients who avoided direct sun exposure for two weeks post-treatment. Long-term follow-up studies indicate that patients maintaining comprehensive sun protection achieve superior aesthetic outcomes with 40% fewer revision treatments required. Meta-analyses of laser treatment studies consistently identify sun exposure as the primary modifiable risk factor for post-treatment complications.
5.3 Guidelines from Leading Aesthetic Societies & Clinics
Professional organizations including the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) and the International Association for Physicians in Aesthetic Medicine provide detailed post-treatment care protocols emphasizing sun protection as a critical component of optimal outcomes. These guidelines recommend minimum SPF 30 broad-spectrum protection, physical sun avoidance during peak hours, and protective clothing for all post-laser patients. Leading aesthetic clinics report implementing mandatory sun protection education and compliance monitoring to reduce complication rates and improve patient satisfaction scores. Industry best practices include providing detailed written instructions, follow-up communication, and patient accountability measures to ensure adherence to sun protection protocols.
6. Practical Tips for Daily Life
Integrating effective sun protection into daily routines requires practical strategies that accommodate lifestyle demands while maintaining treatment integrity.

6.1 Reapply Sunscreen: Timing & Amount
Proper sunscreen reapplication represents one of the most challenging aspects of post-treatment care, requiring specific timing and quantity guidelines for optimal protection. The standard recommendation of 2mg/cm² translates to approximately 1/4 teaspoon for the face and 1 ounce for the entire body. Reapplication every two hours becomes critical during outdoor activities, with additional applications following swimming, sweating, or towel use. Patients should set smartphone reminders for reapplication timing and carry travel-sized sunscreen products for convenient touch-ups. Water-resistant formulations provide extended protection during physical activities but still require reapplication according to manufacturer guidelines. The key is consistent application rather than relying on high SPF numbers without proper reapplication protocols.
6.2 Adjust Outdoor Activities: Morning/Evening Preference
Modifying daily schedules to avoid peak UV intensity hours significantly reduces overall radiation exposure while allowing patients to maintain active lifestyles during the healing period. UV radiation intensity peaks between 10 AM and 4 PM, with approximately 75% of daily UV dose occurring during this window. Early morning activities (before 10 AM) and evening exercise (after 4 PM) provide safer alternatives for outdoor recreation. Patients can utilize UV index forecasts to plan activities during lower-risk periods and seek indoor alternatives during high-intensity days. This temporal modification strategy proves particularly effective for athletic patients who require outdoor training schedules while maintaining treatment compliance.
6.3 Make Sun Safety Part of Your Skincare Routine
Integrating sun protection into established skincare routines ensures consistent application and reduces the likelihood of forgotten protection. Morning skincare sequences should conclude with broad-spectrum sunscreen application as the final step before makeup or daily activities. Evening routines should include gentle cleansing to remove sunscreen residue and allow skin barrier repair overnight. Patients benefit from establishing trigger reminders such as applying sunscreen immediately after moisturizer or before leaving the house. Keeping sunscreen products visible in bathrooms, cars, and workplaces creates environmental cues that promote consistent use. This systematic approach transforms sun protection from a conscious decision into an automatic habit.
6.4 Track Your Skin’s Response & When to Call Your Clinic
Monitoring post-treatment skin responses enables early identification of complications and appropriate intervention timing. Patients should document daily skin appearance, sensitivity levels, and any unusual changes using smartphone photography for objective comparison. Normal healing progression includes gradual reduction of erythema, decreased sensitivity, and restoration of normal skin texture over 1-4 weeks depending on treatment type. Warning signs requiring immediate clinic contact include increasing redness, blistering, severe pain, signs of infection, or development of new pigmentation changes. Establishing clear communication protocols with treatment providers ensures timely intervention when complications arise and provides patients with confidence in their recovery process.
7. Key Takeaways
Post-treatment sun protection is essential to ensure safe, lasting results from laser and RF aesthetic procedures. These treatments make skin temporarily more photosensitive, increasing risks of hyperpigmentation, burns, and slower healing without proper care. Daily broad-spectrum SPF 30–50, avoiding sun during peak hours, and using hats or UPF clothing work together to shield healing skin. Mineral sunscreens (zinc oxide, titanium dioxide) are preferred for sensitive post-laser skin, while chemical sunscreens must be chosen carefully to avoid irritation. Most procedures require strict sun care for 2–8 weeks, but daily sunscreen should remain a lifelong habit. Expert guidelines link good sun protection to higher treatment success and fewer complications. By making sun safety routine, monitoring your skin, and staying in touch with your provider, you protect your investment and maintain healthy, youthful results. The short-term effort delivers significant long-term skin and aesthetic benefits.
8. Preguntas más frecuentes (FAQ)
No. Tanning before treatment increases melanin, raising burn and hyperpigmentation risk, and may delay your session. After treatment, sun or tanning beds can trigger dark spots and burns. Avoid tanning 4–6 weeks before and protect skin 4–8 weeks after.
Some people develop post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially those with darker skin types, hormonal influences or poor sun protection. Even brief UV exposure during healing can trigger pigment changes, highlighting why strict sun care is critical.
One missed day rarely causes permanent harm. Resume sunscreen immediately and avoid more sun. If redness or irritation appears, use gentle moisturizer and cold compresses. Call your clinic if symptoms persist or worsen.
No. Sunscreen is essential but works best when combined with shade, hats, UPF clothing, and avoiding midday sun. Proper application and frequent reapplication are key—physical barriers help cover any gaps in protection.
Extra care is usually needed for 2–8 weeks depending on treatment depth. But daily SPF use should be a lifelong habit to protect your skin and maintain treatment results.
Mineral (physical) sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are best—they soothe sensitive skin and block UV instantly. Avoid alcohol, fragrance, and harsh chemicals during healing; choose hydrating formulas with ceramides or hyaluronic acid.
9. References & Further Reading
- Post-Summer Skin Repair: Using Pico Lasers for Sun Damage Recovery
- Can You Do Laser Hair Removal During Summer?
- Pico Laser Aftercare: The 72-Hour Rule for Optimal Results
- Lipólisis Láser: Una actualización
- La radiofrecuencia mejora las líneas finas faciales por efecto térmico: ¿Daño o Sólo Estimulación?
Actualización sobre el tratamiento fraccionado con láser de picosegundos: histología y aplicaciones clínicas








