1. Introduction: Why Laser Hair Removal Deserves the Truth
Laser hair removal has revolutionized the beauty and medical aesthetics industry, offering millions of people a long-term solution to unwanted hair. However, with popularity comes misinformation, and the internet is flooded with myths that can prevent people from making informed decisions about this highly effective treatment. Understanding the facts versus fiction is crucial for anyone considering this transformative procedure.
1.1 Why Laser Hair Removal Is So Popular—And Misunderstood
The global laser hair removal market has experienced exponential growth, driven by technological advances in diode laser systems and increasing consumer awareness. Modern diode lasers utilize concentrated light beams at specific wavelengths (typically 755nm, 810nm, 940nm, and 1060nm) to target melanin in hair follicles, causing selective photothermolysis that damages the follicular structure while preserving surrounding skin tissue. Despite its proven efficacy, laser hair removal remains one of the most misunderstood cosmetic procedures. The complexity of laser physics, combined with varying treatment protocols and individual skin characteristics, creates fertile ground for misconceptions. Many potential patients rely on anecdotal evidence rather than clinical data, leading to unrealistic expectations and unnecessary anxiety about the procedure.
1.2 Misinformation Online: What You’ve Likely Heard
Social media platforms and beauty forums are rife with unsubstantiated claims about depilación láser. Common misconceptions include beliefs that the treatment is ineffective on darker skin tones, causes cancer, or provides permanent results after a single session. These myths often stem from outdated information about older laser technologies or experiences with unqualified practitioners using substandard equipment. The proliferation of at-home IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) devices has further confused consumers, as many conflate IPL technology with professional diode laser treatments. While both methods target hair follicles, diode lasers offer superior precision, deeper penetration, and better safety profiles, particularly for individuals with darker skin types.
1.3 What We’ll Set Straight in This Guide
This comprehensive guide will systematically debunk the most persistent myths surrounding laser hair removal using evidence-based information from dermatological research and clinical practice. We’ll explore the science behind diode laser technology, address safety concerns, and provide practical guidance for optimal treatment outcomes. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge needed to make an informed decision about whether laser hair removal is right for you.
2. Common Laser Hair Removal Myths—Debunked with Facts
The landscape of laser hair removal is littered with misconceptions that can deter potential patients from pursuing this highly effective treatment. Let’s examine and debunk the most common myths with scientific evidence and clinical expertise.
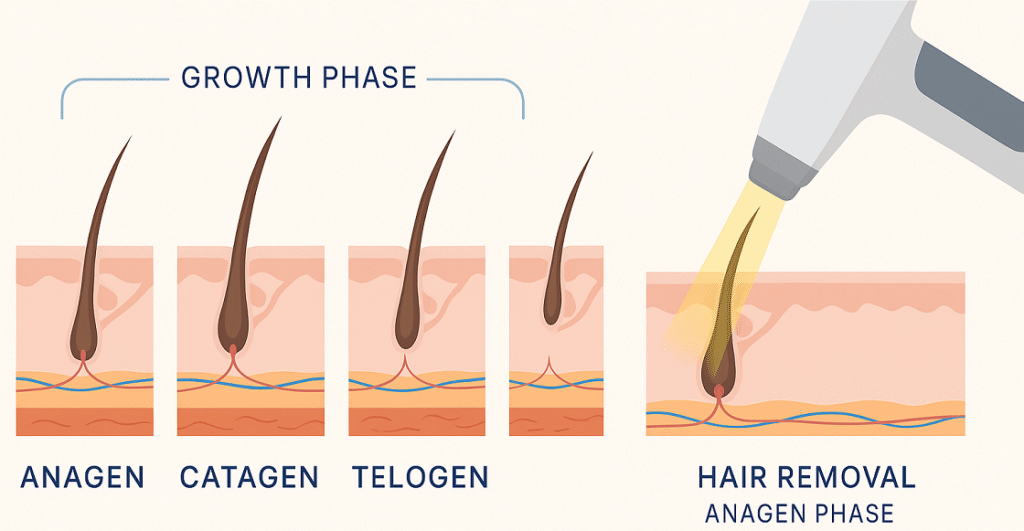
2.1 Myth: Laser Hair Removal Is Permanent After One Session
Laser hair removal can reduce hair counts up to 80%, but multiple sessions are required for optimal results. Hair follicles exist in different growth phases (anagen, catagen, and telogen), and laser energy is most effective during the active anagen phase when melanin concentration is highest. The hair growth cycle varies by body area, with facial hair cycling every 4-6 weeks and body hair every 6-12 weeks. Professional diode laser treatments typically require 6-8 sessions spaced according to the treatment area’s growth cycle. Each session targets actively growing follicles, progressively reducing hair density and thickness. While some follicles may be permanently disabled, others may require maintenance treatments every 6-12 months to maintain optimal results.
2.2 Myth: Laser Hair Removal Doesn’t Work on Dark Skin
Diode lasers remain the gold standard for laser hair removal, especially on darker skin types. Modern diode laser technology has revolutionized treatment possibilities for individuals with higher melanin content in their skin. The key lies in wavelength selection and pulse duration optimization. Combined wavelength diode lasers (810nm, 940nm, and 1060nm) have proven more effective and safer for dark skin types III and IV. Longer wavelengths penetrate deeper into the dermis while causing less epidermal heating, reducing the risk of hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation. Advanced cooling systems and adjustable fluence settings allow skilled practitioners to customize treatments for individual skin types, ensuring both safety and efficacy.
2.3 Myth: It’s Too Painful to Be Worth It
Modern laser technology has significantly improved, with many devices including cooling mechanisms to soothe the skin. Contemporary diode laser systems incorporate sophisticated cooling technologies, including contact cooling, cryogen spray, and air cooling systems that maintain skin surface temperatures below the pain threshold. Most patients describe the sensation as similar to a rubber band snapping against the skin, with discomfort typically lasting only seconds. Pain perception varies by treatment area, with sensitive regions like the bikini line or underarms causing more discomfort than legs or back. Topical anesthetic creams can be applied before treatment for particularly sensitive individuals, though most patients find them unnecessary after the first session.
2.4 Myth: Laser Hair Removal Is Only for Women
The myth that laser hair removal is only for women couldn’t be further from the truth. Male grooming trends have shifted dramatically, with increasing numbers of men seeking laser hair removal for back, chest, shoulders, and facial hair. Professional athletes, bodybuilders, and men in various professions choose laser hair removal for hygiene, comfort, and aesthetic reasons. Men’s hair tends to be coarser and more deeply rooted than women’s, making it an ideal candidate for diode laser treatment. The higher melanin content in male hair follicles allows for more effective energy absorption and follicular destruction. Treatment protocols may require slight modifications in pulse duration and fluence levels to accommodate the structural differences in male hair.
2.5 Myth: It Can Cause Cancer or Damage Your Skin
FDA-approved laser hair removal systems are safe when used by qualified practitioners. Diode lasers emit non-ionizing radiation that cannot penetrate beyond the dermis, making it impossible to affect internal organs or cellular DNA. The specific wavelengths used in hair removal are well-studied and have established safety profiles. Temporary side effects may include mild erythema (redness), perifollicular edema (swelling around hair follicles), and occasional pigmentary changes. Complications such as hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation may occur but are typically transient and resolve within a few months. Serious adverse events are rare and usually result from improper technique, inadequate training, or using non-FDA-approved devices.
3. What to Know Before Starting Laser Hair Removal
Proper preparation and understanding of laser hair removal fundamentals are essential for achieving optimal results while minimizing risks. This section provides comprehensive guidance for prospective patients considering diode laser treatment.
3.1 Choose the Right Laser for Your Skin Type
Diode laser hair removal uses precise wavelengths of light to safely and effectively target hair follicles. Common diode wavelengths—755nm, 810nm, 940nm, and 1060nm—each offer unique benefits. The 810nm wavelength balances melanin absorption and penetration depth, making it ideal for most skin types. For darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick IV–V), longer wavelengths like 940nm and 1060nm reduce the risk of skin damage by reaching deeper without overheating the epidermis. Multi-wavelength systems combine these to enhance results for diverse hair textures and colors. Understanding your Fitzpatrick skin type helps providers choose the safest, most effective laser. For example, patients with type I–III may respond best to 755nm or 810nm, while those with darker skin need safer settings and longer wavelengths. A personalized wavelength plan ensures both optimal hair reduction and skin safety.
3.2 Before You Zap: What to Do and What to Avoid
Proper preparation improves safety and results. Two to four weeks before treatment, stop waxing, tweezing, or threading—these remove the follicle, which the laser needs. Shaving is the only method allowed, and should be done 24–48 hours prior. Sun exposure and tanning increase melanin in the skin, which competes with hair follicles for laser energy and raises burn risk—so stay out of the sun and avoid tanning beds for at least two weeks. Discontinue self-tanners as well. Medications like antibiotics, certain acne treatments, and NSAIDs can increase photosensitivity and should be reviewed with your provider. Hormonal meds that affect hair growth may also influence results. Following these steps ensures safer sessions and better long-term outcomes.
3.3 Aftercare Matters: What Happens Post-Treatment?
After diode laser treatment, temporary redness and swelling are normal signs of the body’s inflammatory response. These symptoms typically fade within a day. Use cool compresses and fragrance-free moisturizers to soothe the skin. For the first 24–48 hours, avoid activities that cause heat or sweat—such as hot showers, saunas, steam rooms, and intense workouts—to reduce irritation. Swimming should also be avoided due to chlorine. In the days that follow, treated hairs will begin to shed naturally over one to three weeks—a process known as delayed hair loss. Do not scratch or pull at the hair; this phase confirms that the laser successfully disrupted follicular growth. Good aftercare supports comfort, reduces side effects, and maximizes your results.

4. Expert Tips: How to Get the Best Results
Maximizing the effectiveness of laser hair removal requires strategic planning, consistent treatment schedules, and professional guidance. These expert recommendations will help you achieve optimal outcomes from your diode laser treatments.
4.1 Stick to the Schedule: Consistency Beats One-Offs
Laser hair removal works best when sessions align with the hair’s anagen (growth) phase—the stage where follicles contain the most melanin. Since not all hairs grow at the same rate, treatments must follow a precise schedule to target the right follicles each time. For facial areas, sessions should occur every 4–6 weeks; for the body, every 6–8 weeks is ideal. Skipping or delaying treatments disrupts this cycle, allowing untreated follicles to survive and potentially requiring more sessions later. Consistency ensures cumulative follicular damage, leading to more thorough and lasting results. Deviating from the schedule is the #1 reason people see slow or uneven progress.
4.2 Ask Questions: Find a Licensed Provider
Always choose a board-certified dermatologist, plastic surgeon, or licensed technician with formal laser training. A qualified provider understands how to treat different skin types safely and can adjust the laser settings accordingly. Confirm the clinic uses FDA-approved devices and follows proper maintenance and safety protocols. Ask about their experience treating patients with similar skin and hair profiles. Essential questions include: What type of laser do you use? How many sessions will I need? What’s your complication rate? Can I see before-and-after photos? A trustworthy provider will offer a consultation, answer openly, and tailor your treatment plan.
4.3 Track Your Glow-Up: Document Progress with Photos
Taking consistent before-and-after photos allows you and your provider to monitor progress objectively. Use the same lighting, angle, and background for each set of images, ideally before every session. Focus on changes in hair thickness, density, and regrowth patterns after 2–3 treatments. These visuals highlight areas responding well—or not—to help adjust energy levels or session intervals. Photos also keep you motivated, especially during slow-progress phases. If patchiness occurs or some areas need additional attention, your provider can respond with more targeted care. Plus, your success story might help others considering treatment.
4.4 Know When to Pause: Pregnancy, Infection, or Active Breakouts
Some conditions require postponing treatment. Pregnancy, though not proven risky, is a common reason to delay laser hair removal due to hormonal shifts that affect hair growth. Active skin infections—bacterial, fungal, or viral—must fully resolve first to avoid spreading or worsening the condition. Herpes outbreaks, in particular, require antiviral precautions. For those with active acne in the treatment area, laser energy could aggravate inflammation or cause scarring. However, laser hair removal often improves conditions like folliculitis and ingrown hairs once flare-ups are controlled. A good provider will advise whether to pause or proceed safely.
5. Final Word: Don’t Let Myths Keep You Hairy
Smooth, hair-free skin doesn’t require guesswork—just accurate information. The myths we’ve busted no longer apply to today’s advanced diode laser systems. When performed by qualified professionals using FDA-approved equipment, laser hair removal is a safe, effective, and long-lasting solution. You’ll save time on daily grooming, reduce irritation from temporary methods, and boost your confidence. Results vary depending on skin tone, hair color, hormones, and treatment consistency—but most patients experience noticeable, lasting hair reduction with proper care. Don’t let outdated fears stop you from exploring this transformative option. Talk to a licensed provider about your skin type, goals, and the best treatment plan. With realistic expectations and commitment, laser hair removal can finally end your battle with unwanted hair—for good.
6. Laser Hair Removal FAQs (Rapid-Fire Truth Bombs)
Not completely—but close! Laser hair removal significantly reduces hair growth long-term. Most people see up to 80–90% reduction after a full treatment series. Occasional touch-ups may be needed as dormant hair follicles can reactivate.
Yes—with the right technology. Diode lasers (especially 810nm, 940nm, and 1060nm) are safe and effective for darker skin tones when used by trained professionals who understand skin type and laser parameters.
Most people describe the sensation as a quick snap—like a rubber band. It’s tolerable, and modern devices use cooling tips or numbing to enhance comfort. Pain levels vary by area and individual sensitivity.
No. Laser hair removal uses non-ionizing radiation, which does not damage DNA or increase cancer risk. Temporary redness or swelling is common, but serious side effects are rare when done properly.
Typically 6–8 sessions spaced 4–8 weeks apart, depending on the treatment area, skin type, and hair thickness. Hormonal areas (like the face) may need more. Consistency is key to long-term results.
Absolutely. Laser hair removal works for all genders. Men commonly treat the back, chest, neck, and beard line for smoother skin or grooming ease. The procedure is just as safe and effective for male hair types.







