1. Введение
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition affecting millions worldwide, characterized by persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, papules, pustules, and, in severe cases, tissue hypertrophy, impacting both appearance and psychological well-being. Traditional treatments often provide incomplete relief and may involve ongoing medication with side effects. The advent of picosecond (pico) laser technology has transformed rosacea management, offering precise treatment of vascular and inflammatory lesions with minimal downtime and high safety. Pico lasers deliver ultra-short pulses measured in trillionths of a second, targeting hemoglobin-rich structures and inflammatory processes while sparing surrounding tissue. This photomechanical mechanism effectively addresses persistent erythema, telangiectasia, and resistant lesions. This review explores the mechanisms, clinical evidence, patient selection, and real-world outcomes of pico laser therapy, highlighting its role in improving disease control and quality of life for individuals managing this challenging dermatological condition.
2. What is Pico Laser?
Pico laser technology represents a groundbreaking advancement in laser dermatology, distinguished from traditional laser systems by its extraordinarily brief pulse durations and unique mechanism of action. While conventional lasers operate in the nanosecond (billionths of a second) or millisecond (thousandths of a second) range, pico lasers deliver energy in picoseconds—one trillionth of a second. This seemingly subtle temporal difference creates profound therapeutic implications, fundamentally altering how laser energy interacts with target tissues and dramatically expanding treatment capabilities while minimizing adverse effects and recovery periods.
2.1 Definition and Overview of Pico Laser Technology
Picosecond laser systems are advanced medical devices that emit ultra-short pulses of coherent light energy, typically operating at wavelengths including 532 nanometers (green light spectrum) and 1064 nanometers (near-infrared spectrum). These wavelengths are specifically selected based on their absorption characteristics by target chromophores—the cellular components that absorb specific light wavelengths. The defining characteristic of pico lasers involves pulse durations ranging from 300 to 750 picoseconds, approximately 100 times shorter than traditional quality-switched (Q-switched) nanosecond lasers. This temporal compression concentrates laser energy delivery, creating intense peak power levels that generate photomechanical rather than predominantly photothermal effects. Pico lasers have gained regulatory approval for treating benign pigmented lesions, удаление татуировок, and increasingly for vascular conditions and омоложение кожи applications including rosacea management.
2.2 How Pico Laser Works: Mechanism of Action
The therapeutic efficacy of pico laser systems derives from sophisticated biophysical interactions between ultra-short laser pulses and target tissue chromophores. Understanding these mechanisms illuminates why pico lasers demonstrate superior outcomes for conditions like rosacea compared to traditional laser modalities.
2.2.1 Ultra-Short Pulses and Photomechanical Effect
The revolutionary aspect of picosecond laser technology lies in its generation of photomechanical effects rather than relying primarily on photothermal tissue destruction. When ultra-short laser pulses interact with target chromophores, the rapid energy delivery creates intense pressure waves and acoustic vibrations that mechanically fracture target structures into microscopic particles. This photoacoustic phenomenon occurs because the pulse duration is shorter than the thermal relaxation time of target tissues—the time required for heat to dissipate from the targeted area. Consequently, minimal thermal diffusion occurs to surrounding tissues, dramatically reducing collateral damage and inflammation. For vascular applications relevant to rosacea treatment, these rapid pulses create selective photothermolysis of dilated blood vessels while preserving adjacent dermal structures. The mechanical fragmentation facilitates enhanced clearance by the body’s lymphatic and immune systems.
2.2.2 Targeting Pigmentation, Vascular Lesions, and Inflammation
Pico laser systems effectively address multiple rosacea manifestations through wavelength-specific chromophore targeting. The 532nm wavelength demonstrates strong absorption by oxyhemoglobin within dilated superficial blood vessels (telangiectasia), making it particularly effective for treating visible facial vascularity characteristic of erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. The 1064nm wavelength penetrates deeper into dermal tissues, targeting larger caliber vessels and addressing deeper vascular networks contributing to persistent erythema. Both wavelengths generate controlled vascular injury through selective photothermolysis, causing vessel coagulation and subsequent absorption by the body. Additionally, the photomechanical effects modulate inflammatory processes by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines, decreasing mast cell degranulation, and promoting tissue remodeling. The ultra-short pulses minimize heat accumulation, making treatments safer for sensitive rosacea-prone skin that typically exhibits heightened reactivity to thermal stimuli. This dual action addresses both vascular and inflammatory components of rosacea pathophysiology.
2.3 Duration, Frequency, and Typical Treatment Sessions
Pico laser treatment protocols for rosacea vary based on disease severity, subtype, and individual patient response characteristics. Individual treatment sessions typically last 15-30 minutes, including preparation time, though actual laser application may only require 5-15 minutes depending on treatment area size. Most dermatologists recommend initial treatment series of 3-6 sessions spaced 4-6 weeks apart to allow adequate healing and vascular remodeling between interventions. Some patients with mild rosacea achieve satisfactory improvement after 2-3 sessions, while those with severe telangiectasia or persistent erythema may require additional treatments for optimal outcomes. Maintenance treatments every 6-12 months help sustain results and prevent disease progression. Energy settings are carefully calibrated based on rosacea severity, skin type, and tolerance, with conservative initial parameters gradually increased as treatment response is assessed.
3. Rosacea and Its Effects on Skin Health
Rosacea represents a chronic inflammatory dermatological disorder characterized by neurovascular dysregulation, immune system abnormalities, and altered cutaneous innate immunity. The condition predominantly affects central facial regions including the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin, though extrafacial manifestations occasionally occur. Understanding rosacea’s complex pathophysiology, diverse clinical presentations, and impact on skin structure and function provides essential context for appreciating how targeted interventions like pico laser therapy address underlying disease mechanisms rather than merely masking superficial symptoms.
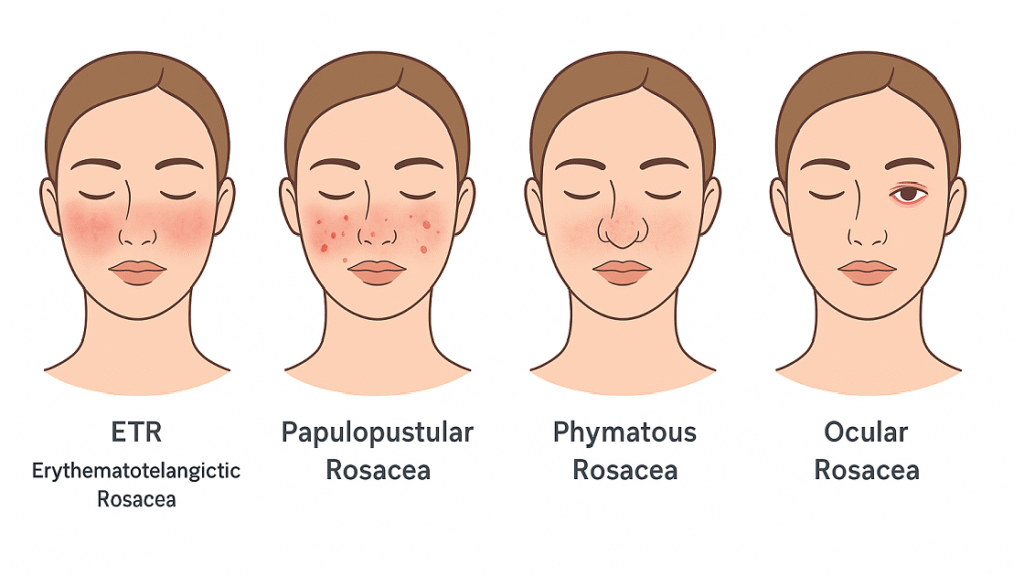
3.1 Types of Rosacea: Erythematotelangiectatic, Papulopustular, Phymatous, Ocular
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): The most common subtype, characterized by persistent facial redness, flushing, visible telangiectasias, and stinging or burning sensations.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Presents with inflammatory papules and pustules resembling acne, along with persistent central facial erythema.
- Phymatous Rosacea: Involves progressive tissue hypertrophy, most notably rhinophyma (bulbous nasal enlargement), but may also affect the forehead, chin, and ears.
- Ocular Rosacea: Affects the eyes and periocular tissues, causing blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
Note: Many patients show overlapping features across subtypes, complicating classification. Pico laser therapy is particularly effective for erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, targeting its vascular component.
3.2 How Rosacea Affects Skin Structure and Function
Rosacea profoundly disrupts normal skin structure and barrier function through multiple pathological mechanisms. The condition causes chronic vasodilation and neovascularization, increasing dermal vessel density and caliber, which manifests as persistent erythema and visible telangiectasia. Inflammatory cell infiltration, particularly neutrophils and lymphocytes, accumulates in perivascular and perifollicular distributions, perpetuating tissue inflammation. The cutaneous barrier becomes compromised, with increased transepidermal water loss, reduced stratum corneum integrity, and altered lipid composition contributing to skin sensitivity and reactivity. Demodex folliculorum mite colonization often increases substantially, with associated inflammatory responses potentially driving disease activity. Altered innate immune responses involving cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides and kallikrein enzymes create inflammatory cascades. Matrix metalloproteinase dysregulation affects collagen integrity, potentially contributing to textural changes and phymatous changes in severe cases. These structural and functional alterations create the visible and symptomatic manifestations that significantly impact quality of life.
3.3 Triggers and Exacerbating Factors
- Temperature extremes, such as hot weather, cold wind, or overheated environments, can worsen rosacea symptoms.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure is a common environmental trigger.
- Hot beverages and spicy foods may provoke facial flushing and irritation.
- Alcoholic drinks, particularly red wine, can exacerbate symptoms.
- Emotional stress and anxiety often trigger flare-ups.
- Strenuous exercise, hot baths, or saunas may increase redness and inflammation.
- Skincare products containing alcohol or fragrances can irritate sensitive skin.
- Topical corticosteroids and certain systemic medications, including vasodilators, may worsen rosacea.
- Hormonal fluctuations, especially during menopause, can influence disease activity.
4. Benefits of Pico Laser for Rosacea
Pico laser technology offers substantial therapeutic advantages for rosacea management, addressing both symptomatic manifestations and underlying pathological mechanisms. The unique characteristics of ultra-short pulse laser systems—particularly the photomechanical effect, precise chromophore targeting, and minimal thermal damage—create ideal conditions for treating the vascular and inflammatory components central to rosacea pathophysiology. The following benefits highlight why pico laser therapy represents an increasingly preferred option for dermatologists and patients seeking effective, safe, and tolerable rosacea interventions.
4.1 Reduction of Redness and Visible Blood Vessels
Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, marked by persistent redness and visible dilated vessels, responds well to pico laser treatment. Ultra-short picosecond pulses selectively target oxyhemoglobin in telangiectasias, causing controlled vascular disruption through photomechanical effects and selective photothermolysis. The 532nm wavelength treats superficial vessels, while 1064nm penetrates deeper networks contributing to background erythema. Clinical studies show many patients achieve 50–80% improvement after treatment series. The photomechanical mechanism fragments vessels for reabsorption rather than relying solely on thermal coagulation, reducing risks of purpura or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Patients report more uniform skin tone and diminished facial vascularity, even in lesions resistant to topical therapy. By targeting both discrete vessels and diffuse redness, pico lasers provide significant aesthetic improvement while minimizing collateral tissue damage, making them a highly effective option for managing vascular manifestations of rosacea.
4.2 Improvement in Skin Texture and Tone
Pico laser therapy enhances skin quality through collagen stimulation and dermal remodeling. Ultra-short pulses create controlled micro-injuries, activating the wound healing cascade without excessive thermal damage. This stimulates fibroblasts to produce collagen and elastin, improving skin texture, smoothness, and overall appearance. The treatment addresses textural irregularities such as papular surface changes and minor phymatous alterations, commonly seen in rosacea. Additionally, it helps even out pigmentary inconsistencies associated with chronic inflammation. The combination of vascular clearance, inflammation modulation, and dermal remodeling results in comprehensive skin improvement beyond simple vessel removal. Patients notice a more refined, youthful, and healthier facial appearance over successive treatments. By integrating multiple mechanisms—collagen induction, tone normalization, and texture enhancement—pico laser therapy offers durable aesthetic benefits while addressing the complex dermatologic features of rosacea in a minimally invasive manner.
4.3 Minimization of Inflammation and Irritation
Pico laser therapy’s photomechanical mechanism provides significant anti-inflammatory benefits for rosacea. Unlike conventional lasers, ultra-short pulses minimize heat generation, reducing collateral tissue damage and inflammatory mediator release. This prevents exacerbation of underlying inflammation, accelerates healing, and improves barrier function. Clinical evidence suggests pico lasers modulate the inflammatory cascade by reducing mast cell degranulation, decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, and regulating cathelicidin-mediated responses. Patients frequently report reduced skin reactivity and sensitivity following treatment. By addressing both vascular and inflammatory pathways, pico laser therapy targets the dual pathophysiology of rosacea, making it effective for patients with coexisting erythematotelangiectatic and inflammatory papulopustular features. Its anti-inflammatory effect complements vascular clearance, supporting long-term symptom control while minimizing irritation and improving overall skin resilience.
4.4 Non-Invasive and Minimal Downtime
Pico laser therapy is non-invasive and requires minimal recovery compared to aggressive lasers or surgical interventions. Treatments involve no incisions, injections, or systemic anesthesia, with topical numbing used only if needed. Post-treatment effects are mild, including transient erythema lasting hours to 1–2 days, occasional mild edema resolving within 24–48 hours, and rarely minor pinpoint purpura. Patients can resume normal activities immediately, needing only sun protection and gentle skincare. Its safety profile allows treatment of extensive facial areas with minimal risk. Compared to traditional vascular lasers that often produce purpura for 7–14 days, pico lasers achieve comparable or superior results with higher tolerability. This combination of efficacy, convenience, and rapid recovery makes pico laser therapy especially suitable for individuals seeking effective rosacea management without significant downtime.
4.5 Suitable for Sensitive Skin
Rosacea-prone skin is often highly sensitive and reactive, complicating treatment. Many therapies can worsen symptoms, but pico laser technology is particularly suitable for sensitive skin. Ultra-short pulses minimize thermal accumulation, reducing discomfort and post-treatment irritation. The photomechanical mechanism elicits less inflammatory response than traditional thermal lasers. Treatment parameters can be tailored to individual tolerance, starting conservatively and gradually increasing intensity. The absence of chemical agents or mechanical abrasion lowers the risk of allergic reactions. Clinical experience demonstrates excellent tolerance even in patients who previously could not endure other laser modalities. By combining efficacy with gentle treatment, pico lasers provide a safe, effective option for managing vascular and inflammatory rosacea features in hypersensitive skin, delivering noticeable improvement without exacerbating underlying skin reactivity.
5. Scientific Evidence Supporting Pico Laser for Rosacea
The clinical application of pico laser technology for rosacea management is supported by a growing body of scientific literature demonstrating efficacy, safety, and patient satisfaction. While research specifically examining picosecond lasers for rosacea remains somewhat limited compared to more established nanosecond vascular lasers, accumulating evidence from clinical trials, case series, and systematic reviews supports pico laser applications for vascular lesions and inflammatory skin conditions relevant to rosacea treatment. Understanding the research landscape helps clinicians and patients make evidence-informed decisions regarding this emerging therapeutic option.
5.1 Key Clinical Studies and Trial Outcomes
Clinical studies of laser therapy for rosacea show strong evidence that vascular-targeting lasers effectively improve symptoms. Research on intense pulsed light and various laser modalities demonstrates excellent to good improvement in most patients with minimal adverse effects. Studies specifically on picosecond lasers indicate efficacy in treating vascular conditions such as telangiectasia and facial redness. In one study, 21 patients achieved excellent improvement and 13 patients good improvement in vascular lesion treatment, highlighting positive overall responses. Investigations using 1064nm pico lasers for skin rejuvenation also report improvements in texture, tone, and vascular appearance. While research specifically on rosacea populations is limited, these findings support the utility of pico lasers in addressing both vascular and inflammatory features of rosacea. Existing evidence indicates that pico lasers are a promising tool for patients with persistent erythema and vascular lesions resistant to conventional treatments.
5.2 Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses on Rosacea Laser Therapy
Systematic reviews consistently demonstrate that laser and light-based therapies effectively reduce erythema, telangiectasia, and inflammatory lesions in rosacea. Meta-analyses of pulsed dye lasers, potassium titanyl phosphate lasers, and intense pulsed light devices show significant improvements in physician-assessed erythema, patient-reported symptom severity, and quality of life. Although systematic reviews of picosecond lasers are emerging, the established evidence for vascular-targeting lasers supports treatment of hemoglobin-rich lesions. Pico lasers offer theoretical advantages over traditional modalities, including reduced thermal damage, faster healing, and improved tolerability for sensitive skin. Ongoing clinical investigations continue to expand the evidence base for pico laser applications, with preliminary data showing outcomes comparable to or exceeding those of established therapies. These findings suggest that pico lasers may provide a safe, effective, and well-tolerated option for managing the vascular and inflammatory components of rosacea.
5.3 Expert Opinions from Dermatologists
Dermatologists and laser specialists increasingly recognize pico lasers as a valuable option for rosacea management. Experts agree that vascular-targeting lasers benefit patients with persistent erythema and telangiectasia resistant to topical or systemic treatments. Pico lasers offer potential advantages over traditional devices, including reduced thermal damage, improved tolerability for sensitive skin, and faster healing. Clinical experience reports high patient satisfaction and adherence to pico laser protocols. Experts emphasize careful patient selection, customized treatment parameters based on skin type and rosacea severity, and realistic outcome expectations. They also note that optimal management often combines laser therapy with topical treatments, trigger avoidance, and gentle skincare. Expert consensus supports considering pico lasers for patients seeking advanced therapeutic options, particularly those who have not achieved satisfactory results with conventional approaches, highlighting the modality’s role in comprehensive rosacea care.
6. Who is a Good Candidate for Pico Laser Treatment?
Determining appropriate candidacy for pico laser therapy requires comprehensive evaluation of individual patient characteristics, rosacea subtype and severity, skin type, medical history, and treatment goals. While pico laser technology demonstrates broad applicability and excellent safety profiles across diverse patient populations, certain factors influence treatment suitability, expected outcomes, and protocol optimization. Healthcare providers should conduct thorough assessments considering the following parameters when recommending pico laser therapy for rosacea management.
6.1 Age and Skin Type Considerations
Pico laser therapy is suitable for adults across a wide age range, from young adults to the elderly, with no strict age limitations. The technology is effective across multiple Fitzpatrick skin types, including fair to medium tones, which traditionally respond well to vascular lasers. Its photomechanical mechanism and minimal thermal damage make treatment safer for darker skin types (IV–V), though careful parameter selection is essential to minimize hyperpigmentation risk. Fairer skin types (I–III) often show more pronounced vascular clearance due to stronger hemoglobin contrast. Elderly patients with photoaging and extensive telangiectasia can achieve substantial improvement, while early intervention in younger patients may help prevent disease progression. Assessment of skin type guides wavelength selection, energy settings, and treatment intervals, optimizing safety and efficacy for individual patients while accommodating variations in vascular visibility, pigmentation, and tissue sensitivity.
6.2 Severity of Rosacea and Symptom Patterns
Pico laser therapy is particularly effective for erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, featuring persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and flushing. Patients with discrete telangiectasia typically experience more dramatic improvements compared to those with diffuse erythema alone. Mild to moderate cases often require fewer treatment sessions, while severe cases with extensive vascularity may need multiple sessions and ongoing maintenance. Papulopustular rosacea benefits from vascular reduction, though inflammatory lesions may need concurrent topical or systemic therapy. Phymatous rosacea may respond to combined approaches addressing vascularity and tissue hypertrophy. Ocular rosacea requires ophthalmologic care, with periocular laser treatments addressing periorbital vascularity. Aligning expectations with specific symptom patterns is essential, as vascular components respond most predictably. Overall, treatment protocols are tailored based on severity, subtype, and individual response to optimize efficacy.

6.3 Contraindications and Precautions
Although pico laser therapy is generally safe, certain contraindications must be considered. Active skin infections, such as herpes simplex, should be resolved or managed prophylactically before treatment. A history of keloid or hypertrophic scarring warrants caution, although risk is lower due to minimal thermal damage. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are relative contraindications. Photosensitizing medications, including tetracyclines, retinoids, and some antibiotics, may increase reactivity and require temporary discontinuation or parameter adjustment. Recent isotretinoin use (within 6–12 months) necessitates careful evaluation. Unrealistic expectations, inability to comply with post-care instructions, or use of vasodilating medications can affect outcomes. Proper patient education and screening ensure safety, optimize results, and minimize complications, making pre-treatment assessment essential for individualized rosacea management.
6.4 Combining Pico Laser with Topical or Oral Treatments
Optimal rosacea management often combines pico laser therapy with topical or oral medications and supportive skincare. Topical agents such as metronidazole, azelaic acid, ivermectin, or brimonidine help control inflammation and erythema, potentially enhancing laser outcomes. Oral antibiotics like doxycycline at anti-inflammatory doses address persistent inflammatory lesions and modulate disease pathways. Photosensitizing topicals, such as retinoids, may be paused during laser therapy and resumed after healing. Gentle, barrier-supportive skincare with ceramide moisturizers, mineral sunscreens, and fragrance-free products maintains skin health and prolongs treatment effects. Identifying and avoiding triggers complements therapy. Treatment sequencing varies: some clinicians start medications before lasers, others begin with laser therapy. Collaborative, multimodal approaches allow individualized care addressing vascular, inflammatory, and textural components of rosacea for comprehensive disease control.
7. Patient Experiences and Testimonials
While clinical research provides objective evidence supporting pico laser efficacy for rosacea, patient perspectives offer invaluable insights into real-world treatment experiences, subjective improvements, and quality of life impacts. Individual testimonials and satisfaction reports, though anecdotal, illuminate practical aspects of treatment tolerance, outcome expectations, and long-term satisfaction that may not be fully captured in controlled clinical trials. Understanding patient experiences helps prospective candidates develop realistic expectations regarding the treatment journey and potential benefits pico laser therapy may provide for managing their rosacea symptoms.
7.1 Real-Life Success Stories
Many rosacea patients report transformative experiences after pico laser treatments. Patients often describe years of persistent redness and visible blood vessels impacting self-confidence, with heavy makeup needed to conceal symptoms. Conventional therapies, including topical metronidazole, oral antibiotics, and skincare regimens, often provide limited improvement, prompting consideration of laser intervention. After 4–6 monthly pico laser sessions, patients typically note progressive reduction in telangiectasia, diminished background erythema, and overall skin improvement. Representative testimonials include statements such as, “After three treatments, my face no longer looks constantly flushed, and visible blood vessels have mostly disappeared,” and, “The treatments were comfortable with minimal downtime, allowing me to schedule sessions during lunch breaks.” These narratives highlight not only aesthetic improvement but also restored confidence and convenience, demonstrating the real-life impact of pico laser therapy on both appearance and daily functioning.
7.2 Improvements in Redness, Texture, and Overall Skin Health
Patient-reported outcomes consistently highlight improvements beyond vascular clearance. Early in treatment, flushing intensity and duration decrease, with reduced reactivity to triggers. Visible telangiectasia often improves after 2–3 sessions, with continued enhancement over the treatment series. Background erythema gradually diminishes, producing a more uniform skin tone. Many patients report smoother, more refined skin texture, reduced sensitivity, and better tolerance of skincare products previously causing irritation. Emotional and psychological benefits are also notable, including increased self-confidence, reduced reliance on concealing makeup, and decreased anxiety in social settings. Satisfaction is generally high, with many patients noting results exceeding expectations. The combination of efficacy, minimal downtime, and tolerability reinforces the practical advantages of pico laser therapy, providing meaningful improvements in both appearance and overall skin health for rosacea sufferers.
7.3 Addressing Skepticism and Expectations
Many patients approach pico laser therapy cautiously after previous treatment failures, expressing concerns about skin sensitivity, treatment discomfort, and temporary versus lasting results. Cost-benefit considerations and fear of worsening symptoms are common. Healthcare providers address these concerns through pre-treatment consultations, explaining photomechanical mechanisms, reviewing before-and-after photos, setting realistic expectations, and offering small test treatments when needed. Most patients report tolerable sensations, typically brief stinging or snapping rather than significant pain. Post-treatment effects are usually mild, with transient redness resolving quickly. Clear expectation-setting emphasizes that while significant improvement is likely, complete vessel elimination may not occur, periodic maintenance may be required, and ongoing trigger avoidance and skincare remain essential. By managing expectations and educating patients, providers help maximize satisfaction and confidence in pico laser therapy for rosacea.
8. Summary of Pico Laser Benefits for Rosacea
Лазерная технология Pico represents a major advancement in rosacea management, offering precise, evidence-based treatment for vascular and inflammatory manifestations. Ultra-short pulses, photomechanical effects, and selective chromophore targeting minimize collateral damage and ensure safety for sensitive skin. The therapy effectively reduces telangiectasia and persistent erythema, with many patients achieving 50–80% improvement, while stimulating collagen and dermal remodeling to enhance texture, tone, and overall skin quality. Anti-inflammatory effects help control disease activity and skin reactivity. Its non-invasive nature and minimal downtime make it convenient for busy lifestyles. Clinical studies, systematic reviews, and expert consensus support its efficacy, particularly for erythematotelangiectatic rosacea resistant to conventional treatments. Patient testimonials report transformative improvements in appearance, confidence, and emotional well-being. When combined with topical or systemic therapies, trigger avoidance, and supportive skincare, pico laser therapy offers a safe, effective, and tolerable option, improving both disease control and quality of life for rosacea sufferers.








